Step into the world of small business retail inventory software, where efficiency meets profitability. Dive into the realm of specialized tools that empower you to streamline operations, optimize stock management, and unlock growth potential like never before.
From cloud-based wonders to on-premise powerhouses, explore the diverse landscape of software solutions tailored to the unique needs of small businesses. Discover the secrets to seamless implementation, cost-effective budgeting, and vendor selection that sets you on the path to retail success.
Software Features
Small business retail inventory software provides a range of essential features to help businesses manage their inventory effectively. These features include:
- Stock management: This feature allows businesses to track their inventory levels, including the quantity of each item in stock, the location of each item, and the cost of each item.
- Order processing: This feature allows businesses to process customer orders, including tracking the status of orders, generating invoices, and managing payments.
- Reporting: This feature allows businesses to generate reports on their inventory, including reports on stock levels, sales trends, and profitability.
Using specialized software for small businesses has several benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency: Inventory software can help businesses to improve their efficiency by automating many of the tasks involved in inventory management, such as tracking stock levels and processing orders.
- Increased accuracy: Inventory software can help businesses to increase the accuracy of their inventory records, which can lead to reduced losses due to theft or spoilage.
- Better customer service: Inventory software can help businesses to provide better customer service by allowing them to track the status of orders and provide accurate information about product availability.
Types of Software
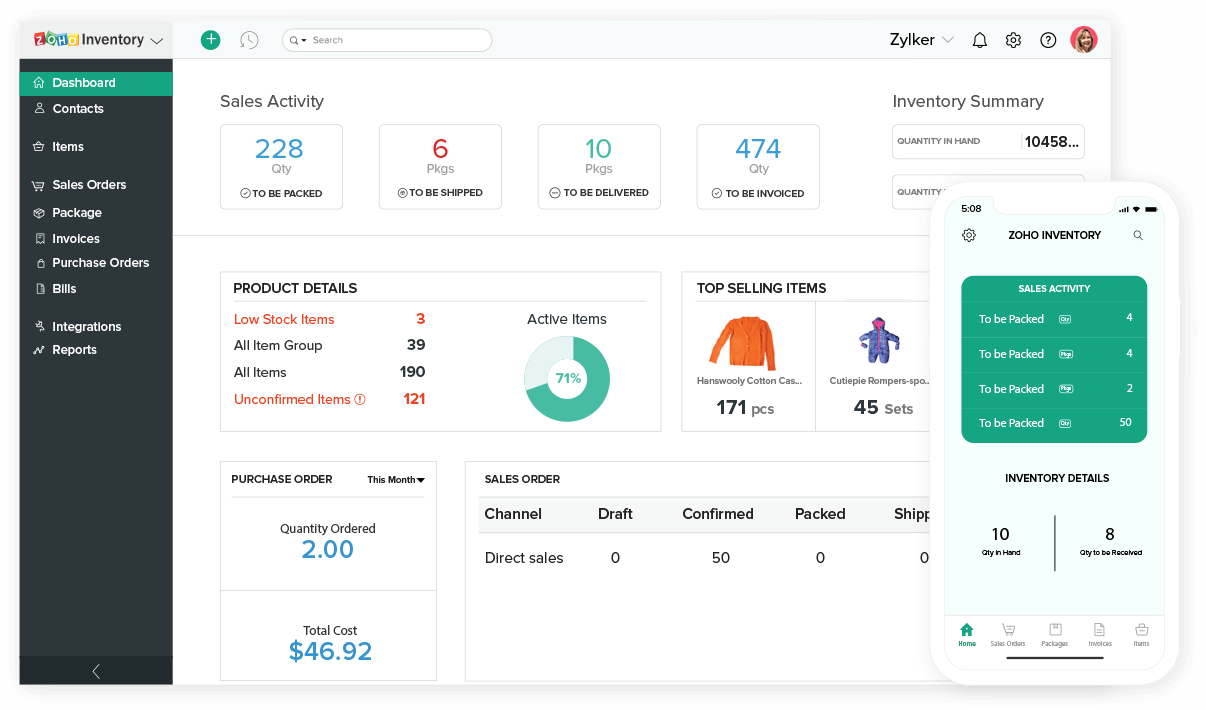
Small business retail inventory software comes in various types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the different options can help you choose the right solution for your business.
The three main types of retail inventory software are cloud-based, on-premise, and hybrid.
Cloud-Based Software
Cloud-based software is hosted on a remote server and accessed through an internet connection. It offers several benefits, including:
- Accessibility: Cloud-based software can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it convenient for remote work or multiple locations.
- Scalability: Cloud-based software can easily scale up or down as your business needs change, eliminating the need for costly hardware upgrades.
- Updates: Cloud-based software is automatically updated by the vendor, ensuring you always have the latest features and security patches.
However, cloud-based software also has some drawbacks:
- Internet dependence: Cloud-based software requires a reliable internet connection to function, which can be a limitation in areas with poor connectivity.
- Security concerns: Storing data on a remote server can raise security concerns, so it’s important to choose a vendor with a strong track record of data protection.
- Limited customization: Cloud-based software is typically less customizable than on-premise software, as vendors may limit modifications to ensure compatibility across multiple users.
On-Premise Software
On-premise software is installed on a local server or computer and managed by the business itself. This type of software offers:
- Control and security: On-premise software gives businesses full control over their data and security measures, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
- Customization: On-premise software can be customized to meet the specific needs of the business, allowing for greater flexibility and functionality.
- Reliability: On-premise software is not dependent on an internet connection, ensuring uninterrupted access to inventory data.
However, on-premise software also has some disadvantages:
- Cost: On-premise software requires a significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and maintenance.
- Maintenance: Businesses are responsible for maintaining and updating on-premise software, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Scalability: On-premise software can be difficult to scale up or down as business needs change, requiring additional hardware or software purchases.
Hybrid Software, Small business retail inventory software
Hybrid software combines the benefits of both cloud-based and on-premise software. It typically involves storing sensitive data on a local server while using the cloud for less critical data and functionality.
Hybrid software offers:
- Flexibility: Hybrid software provides a balance between control and flexibility, allowing businesses to tailor the solution to their specific requirements.
- Security: By storing sensitive data on-premise, hybrid software reduces the risk of data breaches while still allowing access to cloud-based features.
- Scalability: Hybrid software can be scaled up or down as needed, with the cloud component providing additional capacity when required.
However, hybrid software also has some drawbacks:
- Complexity: Hybrid software can be more complex to manage than either cloud-based or on-premise software, as it involves managing both local and cloud components.
- Cost: Hybrid software can be more expensive than either cloud-based or on-premise software, as it requires investment in both local infrastructure and cloud services.
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between the on-premise and cloud components of hybrid software can be challenging, especially during updates or changes.
Implementation and Integration

Implementing retail inventory software for small businesses involves careful planning and execution. This section provides guidance on key aspects of implementation, including data migration, system integration, and staff training.
Data Migration
Data migration is the process of transferring existing inventory data from legacy systems or spreadsheets into the new software. It is crucial to ensure data accuracy and integrity during this process.
*
- Plan and prepare for data migration by identifying all relevant data sources and their formats.
- Clean and validate the data before migration to remove any errors or inconsistencies.
- Test the migration process thoroughly to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
System Integration
Integrating the inventory software with other business systems, such as accounting or e-commerce platforms, streamlines operations and improves efficiency.
*
- Identify the key systems that need to be integrated with the inventory software.
- Determine the specific data that needs to be shared between systems.
- Configure the software to enable seamless data exchange and avoid data duplication.
Staff Training
Proper staff training is essential for successful adoption of the new software.
*
- Provide comprehensive training sessions that cover all aspects of the software’s functionality.
- Involve staff in the implementation process to gain their buy-in and feedback.
- Offer ongoing support and training to ensure staff proficiency and address any issues that may arise.
Cost and Pricing Models
Small business retail inventory software pricing models vary depending on factors such as the software’s features, functionality, and support options. Common pricing models include:
- Subscription-based pricing: A monthly or annual fee that provides access to the software and its features.
- Per-user pricing: A fee charged for each user who accesses the software.
- Tiered pricing: Different pricing plans with varying features and functionality.
- One-time purchase: A single payment that grants perpetual access to the software, with limited or no ongoing support.
Factors Influencing Software Costs
Factors that influence software costs include:
- Number of users: Software with multi-user capabilities typically costs more than single-user versions.
- Features and functionality: Advanced features and integrations can increase the cost of the software.
- Support options: Software with dedicated support, training, and updates may cost more than those with limited support.
- Cloud-based vs. on-premise: Cloud-based software typically requires a subscription fee, while on-premise software requires a one-time purchase and ongoing maintenance costs.
Tips for Budgeting and Cost Optimization
To optimize costs, consider the following tips:
- Evaluate your needs: Determine the specific features and functionality you require before purchasing software.
- Compare pricing models: Choose the pricing model that aligns with your budget and usage patterns.
- Negotiate discounts: Contact vendors to inquire about discounts for multiple users or long-term contracts.
- Consider open-source software: Explore open-source alternatives that offer similar features at a lower cost.
Vendor Selection and Evaluation: Small Business Retail Inventory Software
Selecting the right software vendor is crucial for small businesses. Consider these factors:
- Industry Experience: Choose a vendor with a proven track record in your industry.
- Customer Support: Look for vendors offering responsive and reliable support.
- Scalability: Ensure the software can grow with your business.
- Cost: Consider the software’s cost, licensing fees, and ongoing maintenance.
- Integration: Assess how easily the software integrates with your existing systems.
- Security: Evaluate the vendor’s security measures to protect your data.
- Reputation: Check online reviews and testimonials from other businesses.
Vendor Due Diligence Process
Follow these steps to conduct vendor due diligence:
- Create a Request for Proposal (RFP): Artikel your requirements and invite vendors to submit proposals.
- Evaluate Proposals: Carefully review vendor responses against your criteria.
- Request Demos and References: See the software in action and speak to existing customers.
- Negotiate Contract: Discuss pricing, terms, and service level agreements (SLAs).
- Sign Contract: Formalize your agreement with the selected vendor.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Small businesses have leveraged retail inventory software to enhance their operations and drive growth. Here are a few notable case studies:
- Company A: A small clothing boutique implemented inventory software to manage their growing inventory. The software provided real-time visibility into stock levels, allowing them to optimize ordering and reduce overstocking. As a result, they experienced a 15% increase in sales and a significant reduction in inventory waste.
- Company B: A hardware store struggled with manual inventory tracking, leading to frequent stockouts and customer dissatisfaction. By implementing inventory software, they automated inventory updates, improved stock accuracy, and enhanced customer service. This resulted in a 20% increase in customer satisfaction and a 10% reduction in stockouts.
Key Takeaways
* Retail inventory software can streamline inventory management, reduce errors, and improve stock accuracy.
* Automated inventory updates and real-time visibility enable businesses to optimize ordering and minimize overstocking.
* Improved inventory management leads to increased sales, enhanced customer satisfaction, and reduced waste.
Closing Summary

Embrace the transformative power of small business retail inventory software. Witness how technology becomes your ally, empowering you to conquer inventory challenges, boost customer satisfaction, and propel your business to new heights. Let this guide be your compass, navigating you through the complexities of software selection, implementation, and optimization. Seize the opportunity to transform your retail operations and unlock the full potential of your small business.
FAQ Explained
What are the key benefits of using small business retail inventory software?
Streamlined stock management, improved order processing efficiency, enhanced reporting capabilities, and optimized inventory levels.
What types of small business retail inventory software are available?
Cloud-based, on-premise, and hybrid solutions, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
How do I select the right software vendor for my small business?
Consider factors such as industry experience, customer support, scalability, and pricing.